IN THIS LESSON
Congestive Heart Failure
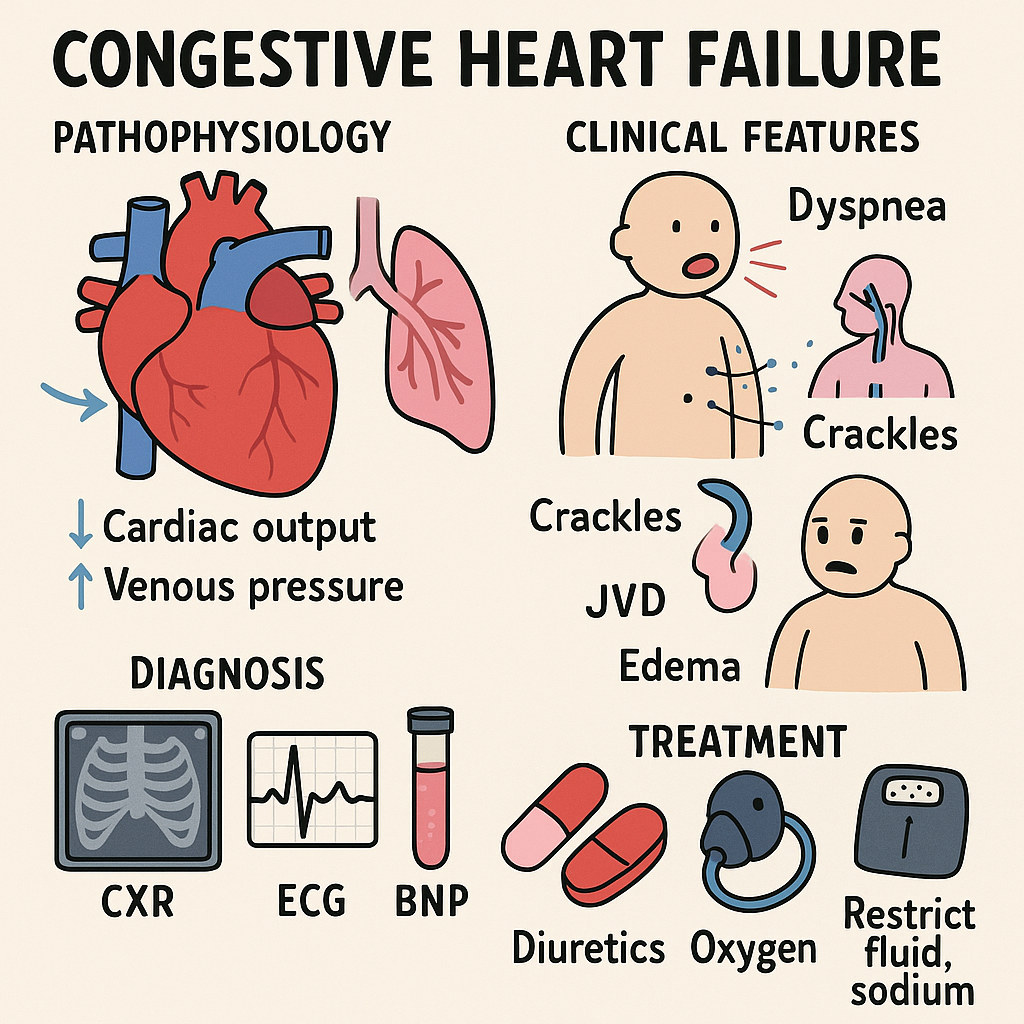
1. Pathophysiology
Definition: Inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood to meet metabolic demands.
Types:
Systolic HF (HFrEF): ↓ contractility → ↓ ejection fraction (<40%).
Diastolic HF (HFpEF): impaired relaxation → normal EF but ↓ filling.
Mechanism:
↓ cardiac output → activation of RAAS → ↑ preload & afterload.
↑ venous pressure → pulmonary & systemic congestion.
2. Clinical Features
Left-sided failure:
Dyspnea on exertion (DOE)
Orthopnea, Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND)
Crackles/rales (pulmonary congestion)
Right-sided failure:
Jugular Venous Distention (JVD)
Hepatomegaly, ascites
Peripheral edema, weight gain
3. Diagnosis
CXR: Cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion, Kerley B lines.
ECG: Ischemia, arrhythmia, LVH, MI changes.
BNP / NT-proBNP: ↑ indicates ventricular stretch.
Echocardiogram: Gold standard for EF, wall motion, diastolic function.
Labs: Check renal function, electrolytes.
4. Treatment
Lifestyle:
Na⁺ < 2g/day, Fluid < 2L/day
Weight monitoring, exercise, vaccination (flu, pneumococcal)
Medications:
ACE-I/ARB/ARNI: ↓ afterload, improve mortality.
Beta-blockers (metoprolol, carvedilol): ↓ mortality, anti-remodeling.
Loop diuretics: Symptomatic relief of congestion.
Aldosterone antagonists (spironolactone, eplerenone): ↓ mortality if EF <35%.
Hydralazine + ISDN: For African Americans or ACE-I intolerance.
SGLT2 inhibitors (dapagliflozin, empagliflozin): Improve outcomes.
Devices:
AICD: EF ≤35% for primary prevention.
CRT: For symptomatic HF with wide QRS (>150 ms).
Advanced:
Inotropes (dobutamine, milrinone) for refractory HF.
LVAD or heart transplant if end-stage.
-
Add a short summary or a list of helpful resources here.